In April 2024, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) finalized workplace protections under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) for methylene chloride to protect human health.
The regulation strives to reduce workers’ exposure to methylene chloride by banning the use and manufacturing of methylene chloride, except for a chosen limited use, such as a research lab.
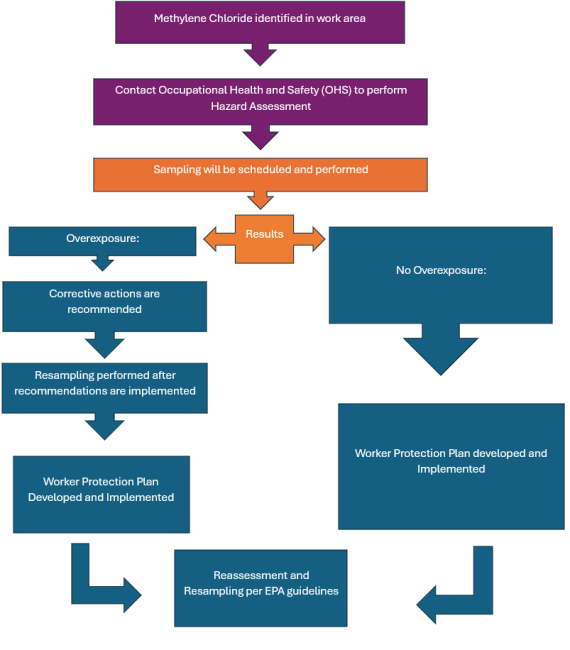
Methylene chloride found in your work area that does not meet the exceptions or is no longer going to be used, will need to be disposed of (see the compliance guide) per guidance from Environmental Management.
If your department plans to keep using Methylene chloride, sampling will need to be performed to ensure exposure limits are being met (see table 1).
More information about the Ruling as well as the banned use and exceptions to the rule can be found in the Compliance Guide.
Basic Facts about Methylene Chloride
- It is colorless liquid and a volatile chemical with a sweet odor
- Its name can appear as Methylene Chloride (MeCl) or Dichloromethane (DCM)
- It is a solvent used in consumer and commercial applications, including adhesives and sealants. Used in the automotive industry as a degreaser and cleaner.
- Methylene chloride’s primary route of exposure is inhalation. Exposures can also occur through the skin, or ingested.
- Employees exposed to methylene chloride are at increased risk of developing cancer, adverse effects on the heart, central nervous system and liver, and skin or eye irritation.